Дальнейшие линии имеют важное значение для поддержания каждого веб -сайта, и управление пересылками становится очень трудным, если специалисты SEO имеют отношение к миллионам страниц.
Примеры ситуаций, в которых вам, возможно, придется реализовать диверсии по шкале:
- Веб -сайт E -Commerce содержит большое количество продуктов, которые больше не продаются.
- Устаревшие страницы публикаций новостей больше не актуальны и не имеют исторической ценности.
- Список списка, который содержит устаревшие предложения.
- Обмен работ, в которых публикации терпят неудачу.
Содержание
Почему это существенно важно?
Это может помочь улучшить пользовательский опыт, консолидировать списки ранжирования и сохранить бюджет Crawl.
Вы можете подумать о NoIndexing, но это не мешает ползанию Googlebot. Он тратит впустую бюджет ползания, когда увеличивается количество страниц.
С точки зрения пользовательского опыта, посадка на устаревшую ссылку разочаровывает. Например, если пользователь оказывается на устаревшем JolistListe, лучше отправить его на следующий матч для активного списка.
В журнале поисковых систем мы получаем много 404 ссылок от AI Chatbots, поскольку галлюцинации изобретают, когда меня изобрели URL -адресами, которые никогда не существовали.
Мы используем Google Analytics 4 и Google Search Console (а иногда и серверные протоколы) для извлечения их 404 страниц и перенаправления их в следующем подходящем контенте на основе статьи Slug.
Когда чат -боты цитируют более 404 страниц, а люди снова и снова проходят разбитые ссылки, это не очень хороший пользовательский опыт.
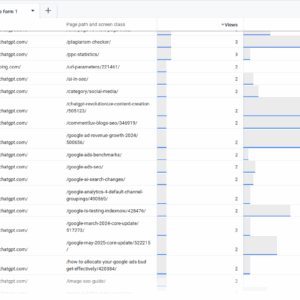
404 Отчет URLS в GSC, май 2025 г.
404 Посещения из AI Chatbots, май 2025 г.
Подготовьте кандидатов
Сначала прочитайте этот пост, чтобы узнать, как создать базу данных вектора Pnecone. (Обратите внимание, что в этом случае мы использовали «Primary_category» в качестве ключа метаданных по сравнению с «категорией».)
Чтобы выполнить эту работу, мы предполагаем, что все векторы вашей статьи уже хранятся в базе данных «Индекс-вертекс».
Подготовьте свой диверсион -Uurls в формате CSV, как в этом Пример файлаПолем Это могут быть существующие статьи, которые вы решили сократить от ваших поисковых консолей или GA4.
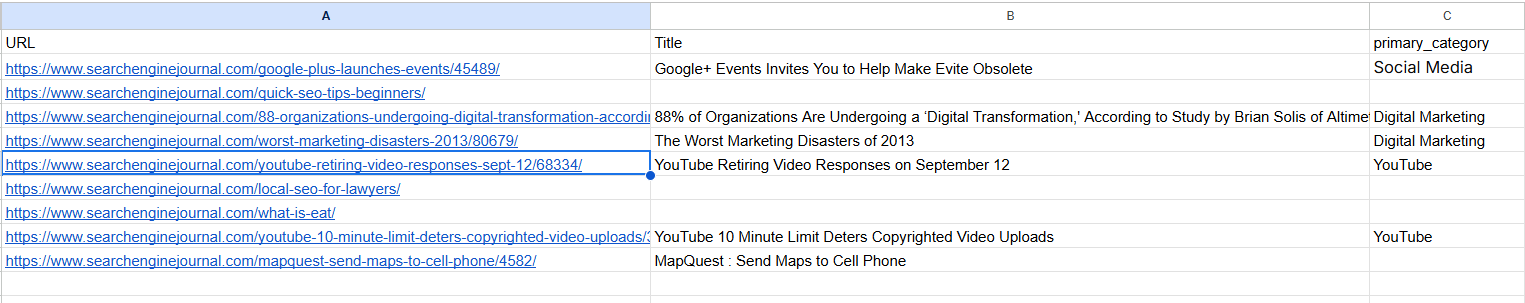 Пример файла с URL -адресами, которые должны быть перенаправлены (снимки экрана с листа Google, май 2025 г.)
Пример файла с URL -адресами, которые должны быть перенаправлены (снимки экрана с листа Google, май 2025 г.)Необязательная информация «Primary_category» — это метаданные, которые доступны с записями данных Pinecone с вашими статьями, когда вы его создали, и могут использоваться для фильтрации элементов из той же категории, что еще больше повышает точность.
Например, если заголовок отсутствует в 404 URL -адресах, сценарий издает слова из URL -адреса извлекает и использует его в качестве входного.
Генерировать перенаправления с помощью Google Vertex AI
Скачать свой Информация о регистрации службы Google API И назовите его как «config.json», пригласите следующий скрипт и Пример файла В том же каталоге в лаборатории Юпитера и выполните его.
import os
import time
import logging
from urllib.parse import urlparse
import re
import pandas as pd
from pandas.errors import EmptyDataError
from typing import Optional, List, Dict, Any
from google.auth import load_credentials_from_file
from google.cloud import aiplatform
from google.api_core.exceptions import GoogleAPIError
from pinecone import Pinecone, PineconeException
from vertexai.language_models import TextEmbeddingModel, TextEmbeddingInput
# Import tenacity for retry mechanism. Tenacity provides a decorator to add retry logic
# to functions, making them more robust against transient errors like network issues or API rate limits.
from tenacity import retry, wait_exponential, stop_after_attempt, retry_if_exception_type
# For clearing output in Jupyter (optional, keep if running in Jupyter).
# This is useful for interactive environments to show progress without cluttering the output.
from IPython.display import clear_output
# ─── USER CONFIGURATION ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────
# Define configurable parameters for the script. These can be easily adjusted
# without modifying the core logic.
INPUT_CSV = "redirect_candidates.csv" # Path to the input CSV file containing URLs to be redirected.
# Expected columns: "URL", "Title", "primary_category".
OUTPUT_CSV = "redirect_map.csv" # Path to the output CSV file where the generated redirect map will be saved.
PINECONE_API_KEY = "YOUR_PINECONE_KEY" # Your API key for Pinecone. Replace with your actual key.
PINECONE_INDEX_NAME = "article-index-vertex" # The name of the Pinecone index where article vectors are stored.
GOOGLE_CRED_PATH = "config.json" # Path to your Google Cloud service account credentials JSON file.
EMBEDDING_MODEL_ID = "text-embedding-005" # Identifier for the Vertex AI text embedding model to use.
TASK_TYPE = "RETRIEVAL_QUERY" # The task type for the embedding model. Try with RETRIEVAL_DOCUMENT vs RETRIEVAL_QUERY to see the difference.
# This influences how the embedding vector is generated for optimal retrieval.
CANDIDATE_FETCH_COUNT = 3 # Number of potential redirect candidates to fetch from Pinecone for each input URL.
TEST_MODE = True # If True, the script will process only a small subset of the input data (MAX_TEST_ROWS).
# Useful for testing and debugging.
MAX_TEST_ROWS = 5 # Maximum number of rows to process when TEST_MODE is True.
QUERY_DELAY = 0.2 # Delay in seconds between successive API queries (to avoid hitting rate limits).
PUBLISH_YEAR_FILTER: List[int] = [] # Optional: List of years to filter Pinecone results by 'publish_year' metadata.
# If empty, no year filtering is applied.
LOG_BATCH_SIZE = 5 # Number of URLs to process before flushing the results to the output CSV.
# This helps in saving progress incrementally and managing memory.
MIN_SLUG_LENGTH = 3 # Minimum length for a URL slug segment to be considered meaningful for embedding.
# Shorter segments might be noise or less descriptive.
# Retry configuration for API calls (Vertex AI and Pinecone).
# These parameters control how the `tenacity` library retries failed API requests.
MAX_RETRIES = 5 # Maximum number of times to retry an API call before giving up.
INITIAL_RETRY_DELAY = 1 # Initial delay in seconds before the first retry.
# Subsequent retries will have exponentially increasing delays.
# ─── SETUP LOGGING ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
# Configure the logging system to output informational messages to the console.
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO, # Set the logging level to INFO, meaning INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL messages will be shown.
format="%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s" # Define the format of log messages (timestamp, level, message).
)
# ─── INITIALIZE GOOGLE VERTEX AI ───────────────────────────────────────────────
# Set the GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS environment variable to point to the
# service account key file. This allows the Google Cloud client libraries to
# authenticate automatically.
os.environ["GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS"] = GOOGLE_CRED_PATH
try:
# Load credentials from the specified JSON file.
credentials, project_id = load_credentials_from_file(GOOGLE_CRED_PATH)
# Initialize the Vertex AI client with the project ID and credentials.
# The location "us-central1" is specified for the AI Platform services.
aiplatform.init(project=project_id, credentials=credentials, location="us-central1")
logging.info("Vertex AI initialized.")
except Exception as e:
# Log an error if Vertex AI initialization fails and re-raise the exception
# to stop script execution, as it's a critical dependency.
logging.error(f"Failed to initialize Vertex AI: {e}")
raise
# Initialize the embedding model once globally.
# This is a crucial optimization for "Resource Management for Embedding Model".
# Loading the model takes time and resources; doing it once avoids repeated loading
# for every URL processed, significantly improving performance.
try:
GLOBAL_EMBEDDING_MODEL = TextEmbeddingModel.from_pretrained(EMBEDDING_MODEL_ID)
logging.info(f"Text Embedding Model '{EMBEDDING_MODEL_ID}' loaded.")
except Exception as e:
# Log an error if the embedding model fails to load and re-raise.
# The script cannot proceed without the embedding model.
logging.error(f"Failed to load Text Embedding Model: {e}")
raise
# ─── INITIALIZE PINECONE ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────
# Initialize the Pinecone client and connect to the specified index.
try:
pinecone = Pinecone(api_key=PINECONE_API_KEY)
index = pinecone.Index(PINECONE_INDEX_NAME)
logging.info(f"Connected to Pinecone index '{PINECONE_INDEX_NAME}'.")
except PineconeException as e:
# Log an error if Pinecone initialization fails and re-raise.
# Pinecone is a critical dependency for finding redirect candidates.
logging.error(f"Pinecone init error: {e}")
raise
# ─── HELPERS ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
def canonical_url(url: str) -> str:
"""
Converts a given URL into its canonical form by:
1. Stripping query strings (e.g., `?param=value`) and URL fragments (e.g., `#section`).
2. Handling URL-encoded fragment markers (`%23`).
3. Preserving the trailing slash if it was present in the original URL's path.
This ensures consistency with the original site's URL structure.
Args:
url (str): The input URL.
Returns:
str: The canonicalized URL.
"""
# Remove query parameters and URL fragments.
temp = url.split('?', 1)[0].split('#', 1)[0]
# Check for URL-encoded fragment markers and remove them.
enc_idx = temp.lower().find('%23')
if enc_idx != -1:
temp = temp[:enc_idx]
# Determine if the original URL path ended with a trailing slash.
has_slash = urlparse(temp).path.endswith('/')
# Remove any trailing slash temporarily for consistent processing.
temp = temp.rstrip('/')
# Re-add the trailing slash if it was originally present.
return temp + ('/' if has_slash else '')
def slug_from_url(url: str) -> str:
"""
Extracts and joins meaningful, non-numeric path segments from a canonical URL
to form a "slug" string. This slug can be used as text for embedding when
a URL's title is not available.
Args:
url (str): The input URL.
Returns:
str: A hyphen-separated string of relevant slug parts.
"""
clean = canonical_url(url) # Get the canonical version of the URL.
path = urlparse(clean).path # Extract the path component of the URL.
segments = [seg for seg in path.split('/') if seg] # Split path into segments and remove empty ones.
# Filter segments based on criteria:
# - Not purely numeric (e.g., '123' is excluded).
# - Length is greater than or equal to MIN_SLUG_LENGTH.
# - Contains at least one alphanumeric character (to exclude purely special character segments).
parts = [seg for seg in segments
if not seg.isdigit()
and len(seg) >= MIN_SLUG_LENGTH
and re.search(r'[A-Za-z0-9]', seg)]
return '-'.join(parts) # Join the filtered parts with hyphens.
# ─── EMBEDDING GENERATION FUNCTION ─────────────────────────────────────────────
# Apply retry mechanism for GoogleAPIError. This makes the embedding generation
# more resilient to transient issues like network problems or Vertex AI rate limits.
@retry(
wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=INITIAL_RETRY_DELAY, min=1, max=10), # Exponential backoff for retries.
stop=stop_after_attempt(MAX_RETRIES), # Stop retrying after a maximum number of attempts.
retry=retry_if_exception_type(GoogleAPIError), # Only retry if a GoogleAPIError occurs.
reraise=True # Re-raise the exception if all retries fail, allowing the calling function to handle it.
)
def generate_embedding(text: str) -> Optional[List[float]]:
"""
Generates a vector embedding for the given text using the globally initialized
Vertex AI Text Embedding Model. Includes retry logic for API calls.
Args:
text (str): The input text (e.g., URL title or slug) to embed.
Returns:
Optional[List[float]]: A list of floats representing the embedding vector,
or None if the input text is empty/whitespace or
if an unexpected error occurs after retries.
"""
if not text or not text.strip():
# If the text is empty or only whitespace, no embedding can be generated.
return None
try:
# Use the globally initialized model to get embeddings.
# This is the "Resource Management for Embedding Model" optimization.
inp = TextEmbeddingInput(text, task_type=TASK_TYPE)
vectors = GLOBAL_EMBEDDING_MODEL.get_embeddings([inp], output_dimensionality=768)
return vectors[0].values # Return the embedding vector (list of floats).
except GoogleAPIError as e:
# Log a warning if a GoogleAPIError occurs, then re-raise to trigger the `tenacity` retry mechanism.
logging.warning(f"Vertex AI error during embedding generation (retrying): {e}")
raise # The `reraise=True` in the decorator will catch this and retry.
except Exception as e:
# Catch any other unexpected exceptions during embedding generation.
logging.error(f"Unexpected error generating embedding: {e}")
return None # Return None for non-retryable or final failed attempts.
# ─── MAIN PROCESSING FUNCTION ─────────────────────────────────────────────────
def build_redirect_map(
input_csv: str,
output_csv: str,
fetch_count: int,
test_mode: bool
):
"""
Builds a redirect map by processing URLs from an input CSV, generating
embeddings, querying Pinecone for similar articles, and identifying
suitable redirect candidates.
Args:
input_csv (str): Path to the input CSV file.
output_csv (str): Path to the output CSV file for the redirect map.
fetch_count (int): Number of candidates to fetch from Pinecone.
test_mode (bool): If True, process only a limited number of rows.
"""
# Read the input CSV file into a Pandas DataFrame.
df = pd.read_csv(input_csv)
required = {"URL", "Title", "primary_category"}
# Validate that all required columns are present in the DataFrame.
if not required.issubset(df.columns):
raise ValueError(f"Input CSV must have columns: {required}")
# Create a set of canonicalized input URLs for efficient lookup.
# This is used to prevent an input URL from redirecting to itself or another input URL,
# which could create redirect loops or redirect to a page that is also being redirected.
input_urls = set(df["URL"].map(canonical_url))
start_idx = 0
# Implement resume functionality: if the output CSV already exists,
# try to find the last processed URL and resume from the next row.
if os.path.exists(output_csv):
try:
prev = pd.read_csv(output_csv)
except EmptyDataError:
# Handle case where the output CSV exists but is empty.
prev = pd.DataFrame()
if not prev.empty:
# Get the last URL that was processed and written to the output file.
last = prev["URL"].iloc[-1]
# Find the index of this last URL in the original input DataFrame.
idxs = df.index[df["URL"].map(canonical_url) == last].tolist()
if idxs:
# Set the starting index for processing to the row after the last processed URL.
start_idx = idxs[0] + 1
logging.info(f"Resuming from row {start_idx} after {last}.")
# Determine the range of rows to process based on test_mode.
if test_mode:
end_idx = min(start_idx + MAX_TEST_ROWS, len(df))
df_proc = df.iloc[start_idx:end_idx] # Select a slice of the DataFrame for testing.
logging.info(f"Test mode: processing rows {start_idx} to {end_idx-1}.")
else:
df_proc = df.iloc[start_idx:] # Process all remaining rows.
logging.info(f"Processing rows {start_idx} to {len(df)-1}.")
total = len(df_proc) # Total number of URLs to process in this run.
processed = 0 # Counter for successfully processed URLs.
batch: List[Dict[str, Any]] = [] # List to store results before flushing to CSV.
# Iterate over each row (URL) in the DataFrame slice to be processed.
for _, row in df_proc.iterrows():
raw_url = row["URL"] # Original URL from the input CSV.
url = canonical_url(raw_url) # Canonicalized version of the URL.
# Get title and category, handling potential missing values by defaulting to empty strings.
title = row["Title"] if isinstance(row["Title"], str) else ""
category = row["primary_category"] if isinstance(row["primary_category"], str) else ""
# Determine the text to use for generating the embedding.
# Prioritize the 'Title' if available, otherwise use a slug derived from the URL.
if title.strip():
text = title
else:
slug = slug_from_url(raw_url)
if not slug:
# If no meaningful slug can be extracted, skip this URL.
logging.info(f"Skipping {raw_url}: insufficient slug context for embedding.")
continue
text = slug.replace('-', ' ') # Prepare slug for embedding by replacing hyphens with spaces.
# Attempt to generate the embedding for the chosen text.
# This call is wrapped in a try-except block to catch final failures after retries.
try:
embedding = generate_embedding(text)
except GoogleAPIError as e:
# If embedding generation fails even after retries, log the error and skip this URL.
logging.error(f"Failed to generate embedding for {raw_url} after {MAX_RETRIES} retries: {e}")
continue # Move to the next URL.
if not embedding:
# If `generate_embedding` returned None (e.g., empty text or unexpected error), skip.
logging.info(f"Skipping {raw_url}: no embedding generated.")
continue
# Build metadata filter for Pinecone query.
# This helps narrow down search results to more relevant candidates (e.g., by category or publish year).
filt: Dict[str, Any] = {}
if category:
# Split category string by comma and strip whitespace for multiple categories.
cats = [c.strip() for c in category.split(",") if c.strip()]
if cats:
filt["primary_category"] = {"$in": cats} # Filter by categories present in Pinecone metadata.
if PUBLISH_YEAR_FILTER:
filt["publish_year"] = {"$in": PUBLISH_YEAR_FILTER} # Filter by specified publish years.
filt["id"] = {"$ne": url} # Exclude the current URL itself from the search results to prevent self-redirects.
# Define a nested function for Pinecone query with retry mechanism.
# This ensures that Pinecone queries are also robust against transient errors.
@retry(
wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=INITIAL_RETRY_DELAY, min=1, max=10),
stop=stop_after_attempt(MAX_RETRIES),
retry=retry_if_exception_type(PineconeException), # Only retry if a PineconeException occurs.
reraise=True # Re-raise the exception if all retries fail.
)
def query_pinecone_with_retry(embedding_vector, top_k_count, pinecone_filter):
"""
Performs a Pinecone index query with retry logic.
"""
return index.query(
vector=embedding_vector,
top_k=top_k_count,
include_values=False, # We don't need the actual vector values in the response.
include_metadata=False, # We don't need the metadata in the response for this logic.
filter=pinecone_filter # Apply the constructed metadata filter.
)
# Attempt to query Pinecone for redirect candidates.
try:
res = query_pinecone_with_retry(embedding, fetch_count, filt)
except PineconeException as e:
# If Pinecone query fails after retries, log the error and skip this URL.
logging.error(f"Failed to query Pinecone for {raw_url} after {MAX_RETRIES} retries: {e}")
continue # Move to the next URL.
candidate = None # Initialize redirect candidate to None.
score = None # Initialize relevance score to None.
# Iterate through the Pinecone query results (matches) to find a suitable candidate.
for m in res.get("matches", []):
cid = m.get("id") # Get the ID (URL) of the matched document in Pinecone.
# A candidate is suitable if:
# 1. It exists (cid is not None).
# 2. It's not the original URL itself (to prevent self-redirects).
# 3. It's not another URL from the input_urls set (to prevent redirecting to a page that's also being redirected).
if cid and cid != url and cid not in input_urls:
candidate = cid # Assign the first valid candidate found.
score = m.get("score") # Get the relevance score of this candidate.
break # Stop after finding the first suitable candidate (Pinecone returns by relevance).
# Append the results for the current URL to the batch.
batch.append({"URL": url, "Redirect Candidate": candidate, "Relevance Score": score})
processed += 1 # Increment the counter for processed URLs.
msg = f"Mapped {url} → {candidate}"
if score is not None:
msg += f" ({score:.4f})" # Add score to log message if available.
logging.info(msg) # Log the mapping result.
# Periodically flush the batch results to the output CSV.
if processed % LOG_BATCH_SIZE == 0:
out_df = pd.DataFrame(batch) # Convert the current batch to a DataFrame.
# Determine file mode: 'a' (append) if file exists, 'w' (write) if new.
mode="a" if os.path.exists(output_csv) else 'w'
# Determine if header should be written (only for new files).
header = not os.path.exists(output_csv)
# Write the batch to the CSV.
out_df.to_csv(output_csv, mode=mode, header=header, index=False)
batch.clear() # Clear the batch after writing to free memory.
if not test_mode:
# clear_output(wait=True) # Uncomment if running in Jupyter and want to clear output
clear_output(wait=True)
print(f"Progress: {processed} / {total}") # Print progress update.
time.sleep(QUERY_DELAY) # Pause for a short delay to avoid overwhelming APIs.
# After the loop, write any remaining items in the batch to the output CSV.
if batch:
out_df = pd.DataFrame(batch)
mode="a" if os.path.exists(output_csv) else 'w'
header = not os.path.exists(output_csv)
out_df.to_csv(output_csv, mode=mode, header=header, index=False)
logging.info(f"Completed. Total processed: {processed}") # Log completion message.
if __name__ == "__main__":
# This block ensures that build_redirect_map is called only when the script is executed directly.
# It passes the user-defined configuration parameters to the main function.
build_redirect_map(INPUT_CSV, OUTPUT_CSV, CANDIDATE_FETCH_COUNT, TEST_MODE)
Вы увидите тест только с пятью записями данных и увидите новый файл под названием «redirect_map.csv», который содержит предложения по обходу.
Как только вы убедитесь, что код проведен плавно, вы можете определить их TEST_MODE Логический слишком верный False И выполнить сценарий для всех ваших URL -адресов.
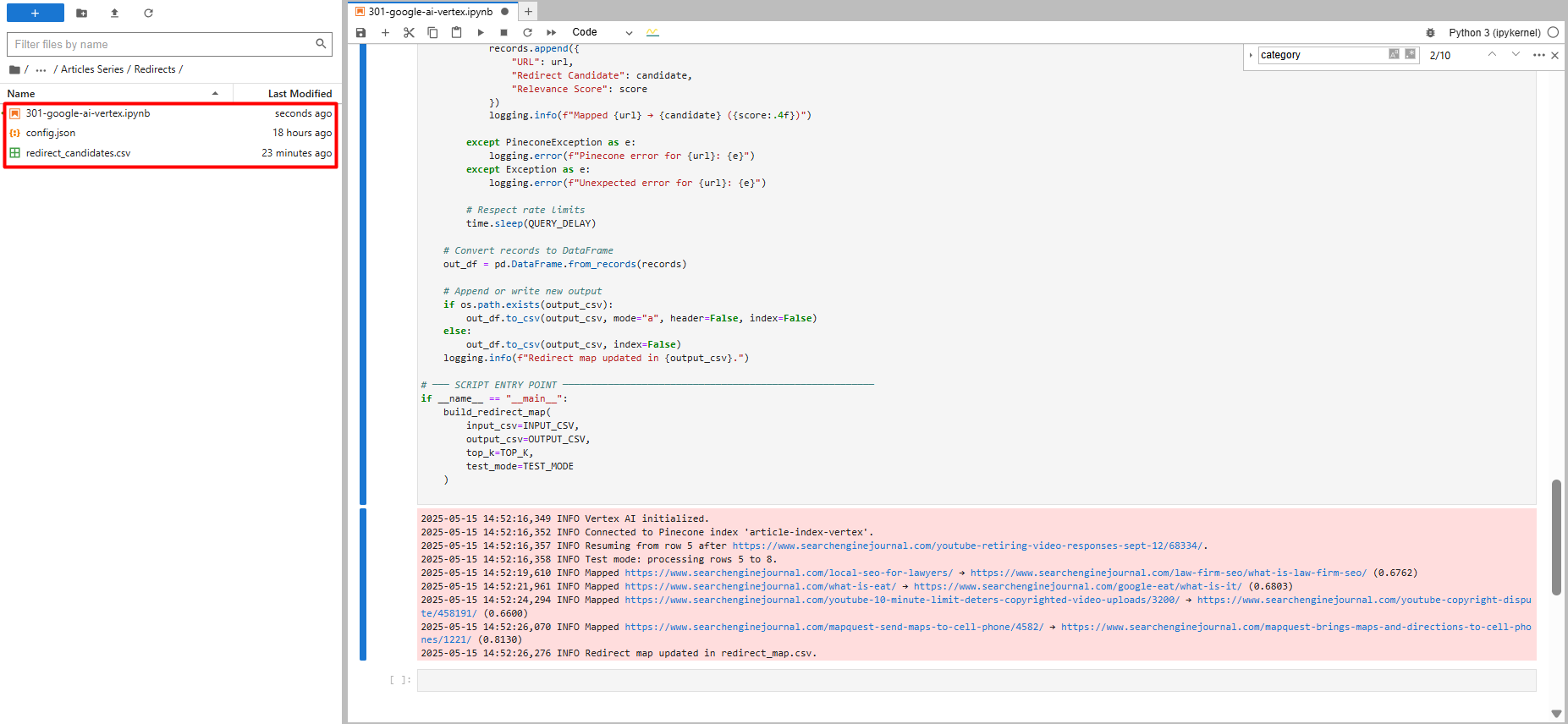 Тестовый запуск только с пятью записями данных (изображение автора, май 2025 г.)
Тестовый запуск только с пятью записями данных (изображение автора, май 2025 г.)Когда код останавливается и возобновит его, он поднимает, где он остановился. Он также проверяет все отвлечения, которые он находит в файле CSV.
Этот обзор предотвращает выбор URL базы данных в обрезанном списке. Выбор такого URL может вызвать бесконечную петлю диверсии.
Для наших URL -адресов отбора проб, вывод отображается ниже.
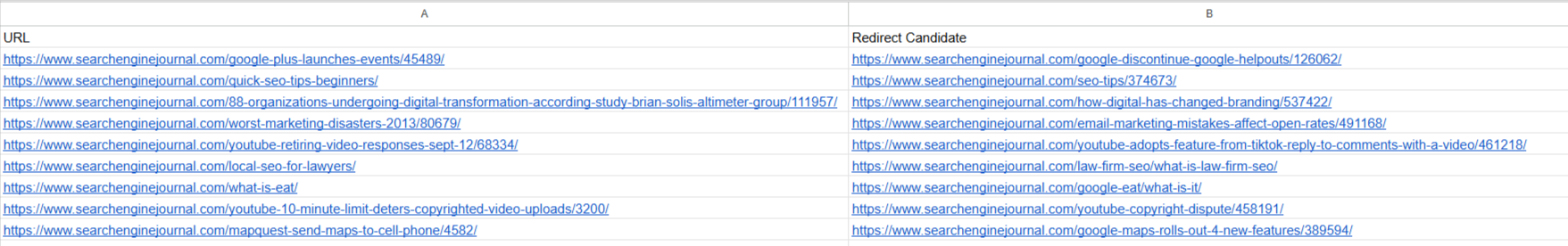 Исправил кандидатов с помощью Google Vertex Ai Ai ararauval_quey (картина автора, май 2025 г.).
Исправил кандидатов с помощью Google Vertex Ai Ai ararauval_quey (картина автора, май 2025 г.).Теперь мы можем импортировать эту карту диверсии в наш менеджер перенаправления в системе управления контентом (CMS), и все!
Вы можете увидеть, как это было, статья 2013 года в более новой, очень актуальной статье «Ответы на пенсию на YouTube 12 сентября» о более новой, очень актуальной статье «YouTube приняла функцию Tikok — ответьте на комментарии с видео».
Он также обнаружил соглашение с «/ogle-eat/», которое является идеальным соглашением на 100%.
Это связано не только за производительность качества Google Vertex LLM, но и с результатом выбора правильных параметров.
Если я «вызову» в качестве типа задачи для создания запроса корицы для статьи YouTube -News, показанной выше, он согласен с «YouTube расширяет вклад сообщества для большего количества создателей», что все еще актуально, но не так хорошо, как и другой.
Для «/что-то есть/», это соответствует статье »/Renmagining-Eeat-to-Drive-High-Sales и поиска/545790/», что не так хорошо, как «/Google-Eat/What-It-It/».
Если вы хотите найти соглашения о выписке из своего свежего пула статей, вы можете запросить Pinecone с помощью дополнительного фильтра метаданных «publish_year», если у вас есть это поле метаданных в ваших записях Pnecone, которые я настоятельно рекомендую.
В коде это PUBLISH_YEAR_FILTER Переменная.
Если у вас есть publish_year Метаданные, вы можете определить годы как значения массива и привлечь статьи в указанные годы.
Генерировать перенаправления с помощью текстовых постельных принадлежностей Openai
Давайте сделаем ту же задачу с моделью «Text-Embedding-Ada-Ada-Ada-002» Openai. Цель состоит в том, чтобы показать начальную разницу Google Vertex AI.
Просто создайте новый файл ноутбуков в том же каталоге, скопируйте этот код, добавьте его и выполните его.
import os
import time
import logging
from urllib.parse import urlparse
import re
import pandas as pd
from pandas.errors import EmptyDataError
from typing import Optional, List, Dict, Any
from openai import OpenAI
from pinecone import Pinecone, PineconeException
# Import tenacity for retry mechanism. Tenacity provides a decorator to add retry logic
# to functions, making them more robust against transient errors like network issues or API rate limits.
from tenacity import retry, wait_exponential, stop_after_attempt, retry_if_exception_type
# For clearing output in Jupyter (optional, keep if running in Jupyter)
from IPython.display import clear_output
# ─── USER CONFIGURATION ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────
# Define configurable parameters for the script. These can be easily adjusted
# without modifying the core logic.
INPUT_CSV = "redirect_candidates.csv" # Path to the input CSV file containing URLs to be redirected.
# Expected columns: "URL", "Title", "primary_category".
OUTPUT_CSV = "redirect_map.csv" # Path to the output CSV file where the generated redirect map will be saved.
PINECONE_API_KEY = "YOUR_PINECONE_API_KEY" # Your API key for Pinecone. Replace with your actual key.
PINECONE_INDEX_NAME = "article-index-ada" # The name of the Pinecone index where article vectors are stored.
OPENAI_API_KEY = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY" # Your API key for OpenAI. Replace with your actual key.
OPENAI_EMBEDDING_MODEL_ID = "text-embedding-ada-002" # Identifier for the OpenAI text embedding model to use.
CANDIDATE_FETCH_COUNT = 3 # Number of potential redirect candidates to fetch from Pinecone for each input URL.
TEST_MODE = True # If True, the script will process only a small subset of the input data (MAX_TEST_ROWS).
# Useful for testing and debugging.
MAX_TEST_ROWS = 5 # Maximum number of rows to process when TEST_MODE is True.
QUERY_DELAY = 0.2 # Delay in seconds between successive API queries (to avoid hitting rate limits).
PUBLISH_YEAR_FILTER: List[int] = [] # Optional: List of years to filter Pinecone results by 'publish_year' metadata eg. [2024,2025].
# If empty, no year filtering is applied.
LOG_BATCH_SIZE = 5 # Number of URLs to process before flushing the results to the output CSV.
# This helps in saving progress incrementally and managing memory.
MIN_SLUG_LENGTH = 3 # Minimum length for a URL slug segment to be considered meaningful for embedding.
# Shorter segments might be noise or less descriptive.
# Retry configuration for API calls (OpenAI and Pinecone).
# These parameters control how the `tenacity` library retries failed API requests.
MAX_RETRIES = 5 # Maximum number of times to retry an API call before giving up.
INITIAL_RETRY_DELAY = 1 # Initial delay in seconds before the first retry.
# Subsequent retries will have exponentially increasing delays.
# ─── SETUP LOGGING ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
# Configure the logging system to output informational messages to the console.
logging.basicConfig(
level=logging.INFO, # Set the logging level to INFO, meaning INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL messages will be shown.
format="%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s" # Define the format of log messages (timestamp, level, message).
)
# ─── INITIALIZE OPENAI CLIENT & PINECONE ───────────────────────────────────────
# Initialize the OpenAI client once globally. This handles resource management efficiently
# as the client object manages connections and authentication.
client = OpenAI(api_key=OPENAI_API_KEY)
try:
# Initialize the Pinecone client and connect to the specified index.
pinecone = Pinecone(api_key=PINECONE_API_KEY)
index = pinecone.Index(PINECONE_INDEX_NAME)
logging.info(f"Connected to Pinecone index '{PINECONE_INDEX_NAME}'.")
except PineconeException as e:
# Log an error if Pinecone initialization fails and re-raise.
# Pinecone is a critical dependency for finding redirect candidates.
logging.error(f"Pinecone init error: {e}")
raise
# ─── HELPERS ───────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
def canonical_url(url: str) -> str:
"""
Converts a given URL into its canonical form by:
1. Stripping query strings (e.g., `?param=value`) and URL fragments (e.g., `#section`).
2. Handling URL-encoded fragment markers (`%23`).
3. Preserving the trailing slash if it was present in the original URL's path.
This ensures consistency with the original site's URL structure.
Args:
url (str): The input URL.
Returns:
str: The canonicalized URL.
"""
# Remove query parameters and URL fragments.
temp = url.split('?', 1)[0]
temp = temp.split('#', 1)[0]
# Check for URL-encoded fragment markers and remove them.
enc_idx = temp.lower().find('%23')
if enc_idx != -1:
temp = temp[:enc_idx]
# Determine if the original URL path ended with a trailing slash.
preserve_slash = temp.endswith('/')
# Strip trailing slash if not originally present.
if not preserve_slash:
temp = temp.rstrip('/')
return temp
def slug_from_url(url: str) -> str:
"""
Extracts and joins meaningful, non-numeric path segments from a canonical URL
to form a "slug" string. This slug can be used as text for embedding when
a URL's title is not available.
Args:
url (str): The input URL.
Returns:
str: A hyphen-separated string of relevant slug parts.
"""
clean = canonical_url(url) # Get the canonical version of the URL.
path = urlparse(clean).path # Extract the path component of the URL.
segments = [seg for seg in path.split('/') if seg] # Split path into segments and remove empty ones.
# Filter segments based on criteria:
# - Not purely numeric (e.g., '123' is excluded).
# - Length is greater than or equal to MIN_SLUG_LENGTH.
# - Contains at least one alphanumeric character (to exclude purely special character segments).
parts = [seg for seg in segments
if not seg.isdigit()
and len(seg) >= MIN_SLUG_LENGTH
and re.search(r'[A-Za-z0-9]', seg)]
return '-'.join(parts) # Join the filtered parts with hyphens.
# ─── EMBEDDING GENERATION FUNCTION ─────────────────────────────────────────────
# Apply retry mechanism for OpenAI API errors. This makes the embedding generation
# more resilient to transient issues like network problems or API rate limits.
@retry(
wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=INITIAL_RETRY_DELAY, min=1, max=10), # Exponential backoff for retries.
stop=stop_after_attempt(MAX_RETRIES), # Stop retrying after a maximum number of attempts.
retry=retry_if_exception_type(Exception), # Retry on any Exception from OpenAI client (can be refined to openai.APIError if desired).
reraise=True # Re-raise the exception if all retries fail, allowing the calling function to handle it.
)
def generate_embedding(text: str) -> Optional[List[float]]:
"""
Generate a vector embedding for the given text using OpenAI's text-embedding-ada-002
via the globally initialized OpenAI client. Includes retry logic for API calls.
Args:
text (str): The input text (e.g., URL title or slug) to embed.
Returns:
Optional[List[float]]: A list of floats representing the embedding vector,
or None if the input text is empty/whitespace or
if an unexpected error occurs after retries.
"""
if not text or not text.strip():
# If the text is empty or only whitespace, no embedding can be generated.
return None
try:
resp = client.embeddings.create( # Use the globally initialized OpenAI client to get embeddings.
model=OPENAI_EMBEDDING_MODEL_ID,
input=text
)
return resp.data[0].embedding # Return the embedding vector (list of floats).
except Exception as e:
# Log a warning if an OpenAI error occurs, then re-raise to trigger the `tenacity` retry mechanism.
logging.warning(f"OpenAI embedding error (retrying): {e}")
raise # The `reraise=True` in the decorator will catch this and retry.
# ─── MAIN PROCESSING FUNCTION ─────────────────────────────────────────────────
def build_redirect_map(
input_csv: str,
output_csv: str,
fetch_count: int,
test_mode: bool
):
"""
Builds a redirect map by processing URLs from an input CSV, generating
embeddings, querying Pinecone for similar articles, and identifying
suitable redirect candidates.
Args:
input_csv (str): Path to the input CSV file.
output_csv (str): Path to the output CSV file for the redirect map.
fetch_count (int): Number of candidates to fetch from Pinecone.
test_mode (bool): If True, process only a limited number of rows.
"""
# Read the input CSV file into a Pandas DataFrame.
df = pd.read_csv(input_csv)
required = {"URL", "Title", "primary_category"}
# Validate that all required columns are present in the DataFrame.
if not required.issubset(df.columns):
raise ValueError(f"Input CSV must have columns: {required}")
# Create a set of canonicalized input URLs for efficient lookup.
# This is used to prevent an input URL from redirecting to itself or another input URL,
# which could create redirect loops or redirect to a page that is also being redirected.
input_urls = set(df["URL"].map(canonical_url))
start_idx = 0
# Implement resume functionality: if the output CSV already exists,
# try to find the last processed URL and resume from the next row.
if os.path.exists(output_csv):
try:
prev = pd.read_csv(output_csv)
except EmptyDataError:
# Handle case where the output CSV exists but is empty.
prev = pd.DataFrame()
if not prev.empty:
# Get the last URL that was processed and written to the output file.
last = prev["URL"].iloc[-1]
# Find the index of this last URL in the original input DataFrame.
idxs = df.index[df["URL"].map(canonical_url) == last].tolist()
if idxs:
# Set the starting index for processing to the row after the last processed URL.
start_idx = idxs[0] + 1
logging.info(f"Resuming from row {start_idx} after {last}.")
# Determine the range of rows to process based on test_mode.
if test_mode:
end_idx = min(start_idx + MAX_TEST_ROWS, len(df))
df_proc = df.iloc[start_idx:end_idx] # Select a slice of the DataFrame for testing.
logging.info(f"Test mode: processing rows {start_idx} to {end_idx-1}.")
else:
df_proc = df.iloc[start_idx:] # Process all remaining rows.
logging.info(f"Processing rows {start_idx} to {len(df)-1}.")
total = len(df_proc) # Total number of URLs to process in this run.
processed = 0 # Counter for successfully processed URLs.
batch: List[Dict[str, Any]] = [] # List to store results before flushing to CSV.
# Iterate over each row (URL) in the DataFrame slice to be processed.
for _, row in df_proc.iterrows():
raw_url = row["URL"] # Original URL from the input CSV.
url = canonical_url(raw_url) # Canonicalized version of the URL.
# Get title and category, handling potential missing values by defaulting to empty strings.
title = row["Title"] if isinstance(row["Title"], str) else ""
category = row["primary_category"] if isinstance(row["primary_category"], str) else ""
# Determine the text to use for generating the embedding.
# Prioritize the 'Title' if available, otherwise use a slug derived from the URL.
if title.strip():
text = title
else:
raw_slug = slug_from_url(raw_url)
if not raw_slug or len(raw_slug) В то время как качество выход Может считаться удовлетворительным, это не качество, которое наблюдается в Google Vertex AI.
В таблице вы найдете разницу в стартовом качестве.
| URL | Google Vertex | Открытый ИИ |
| /Wis-ise/ | /Google-Eat/What-It /// | /5 вкуса, что вы—r-and-to-improve-your-for-google/408423/ |
| /Местный Seo-for-lawyers/ | /Law-Firm-seo/что-то встал | / |
Когда дело доходит до SEO, хотя AI Google Vertex Ai находится в три раза дороже, чем модель Openai, я предпочитаю вершину.
Качество результатов значительно выше. Хотя вы можете предположить более высокие затраты на единицу редактирования текста, вы получаете выгоду от превосходного начального качества, что означает, что результаты напрямую сохраняют ценное время для проверки и проверки результатов.
По моему опыту, для обработки 20 000 URL -адресов Google Vertex AI стоит около 0,04 доллара США.
Это должно быть дороже, но это все еще смехотворно дешево, и вы не должны беспокоиться, если вы справляетесь с задачами с несколькими тысячами URL.
При обработке 1 миллиона URL -адреса прогнозируемая цена составит приблизительно 2 доллара США.
Если вы продолжаете хотеть бесплатный метод, используйте модели BERT и LAMA, чтобы обнять лицо, чтобы генерировать векторные коды без платы за вызов Pro API.
Фактические затраты поступают от вычислительной мощности, необходимой для выполнения моделей, и вы должны генерировать векторное постельное белье всех статей в Pinecone или другой базе данных Vectord с этими моделями, если вы можете запросить векторы, созданные из Bert или Llama.
Таким образом: ИИ — ее могущественный союзник
С помощью ИИ вы можете масштабировать свои SEO или маркетинговые усилия и автоматизировать самые утомительные задачи.
Это не заменяет ваш опыт. Он был разработан, чтобы улучшить их навыки и представить им большие навыки с проблемами и сделать процесс более привлекательным и веселым.
Освоение этих инструментов имеет важное значение для успеха. Я с энтузиазмом пишу о этой теме, чтобы помочь начинающим, учиться вдохновению и чувствовать себя вдохновленным.
Если мы продвигаемся в этой серии, мы рассмотрим, как Google Vertex AI используется для создания внутреннего плагина ссылки.
Больше ресурсов:
Выбранная картина: лучший лес/shutterstock